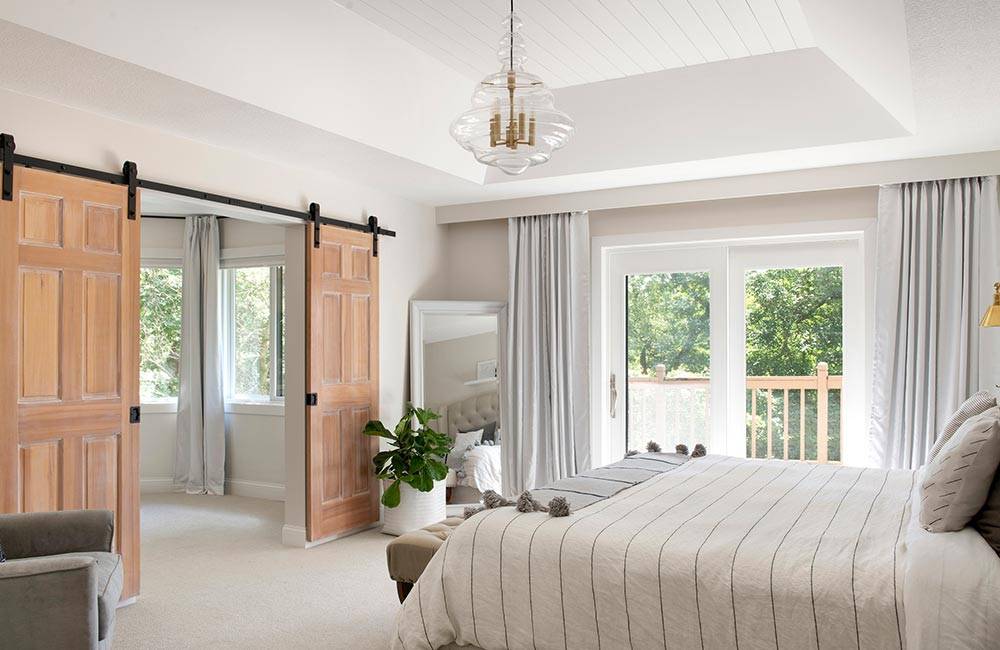
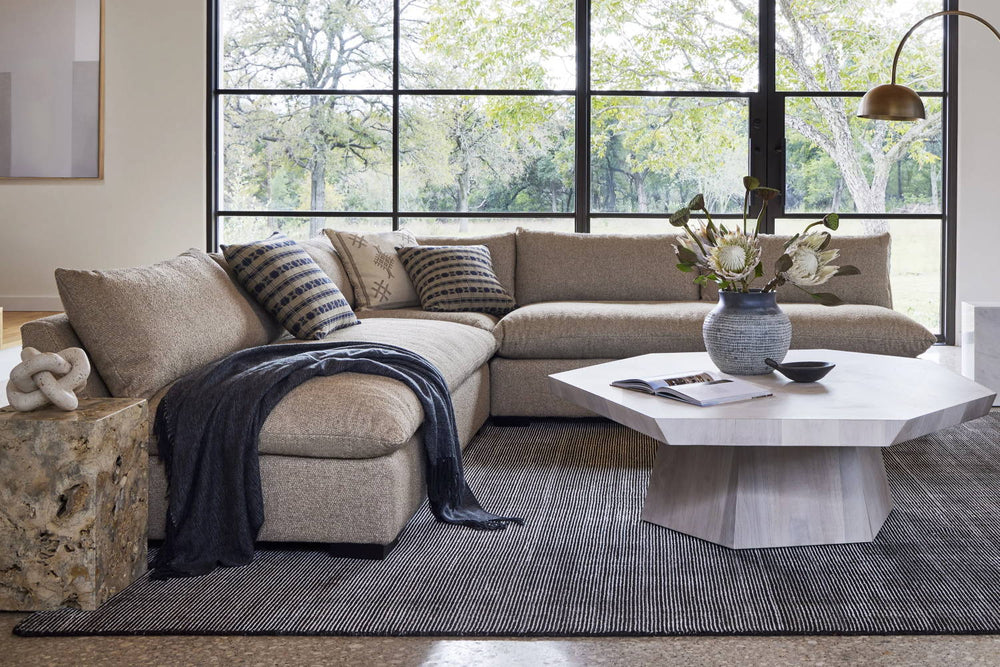
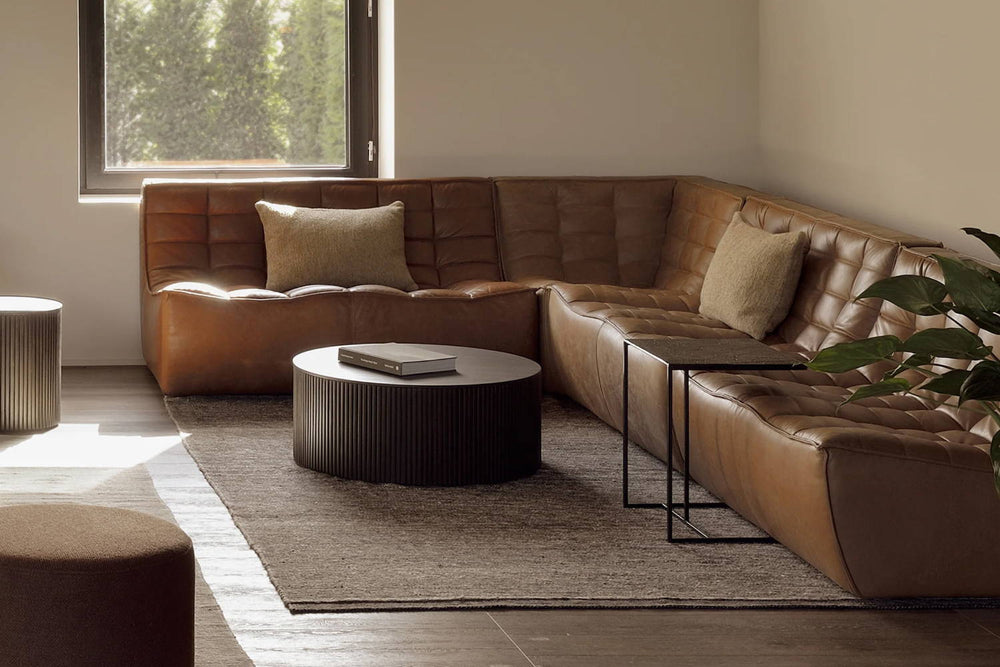
No longer the wave of the future, but the illuminating standard of the here and now, LED lighting offers top-tier technology for a more powerful and eco-friendly lighting experience.
Why is LED Lighting Better?
Here are the top reasons to get you started in making the switch to LED lighting.
Brightness: Unlike traditional lighting, LED lighting is measured in lumens, not watts.
Efficiency: Compared to traditional incandescent lamps, LED lighting has a longer lifespan, is much more durable, and is over five times more efficient. LED bulbs will typically only use 2 to 10 watts of electricity.
Cost: While LED lighting does have a higher upfront cost, they will have a greater lifespan in the long run, passing on savings in many areas.
Design: An incredible design element thanks to their ultra-compact size, LEDs allow designers to create silhouettes, shapes, and fixtures that before would not have been possible.
Temperature: LEDs convert electricity to light without causing any sort of heat build-up.
Mercury free: Mercury is not used in the manufacturing of LED lighting.
Dimming: With earlier technology, LEDs did not “dim” in the way traditional, incandescent lights did, but times have changed. More and more fixtures now offer a “warm dim,” which lowers both the light output, and the color temperature.
Slow failure: LEDs are designed to slowly dim over time towards the end of their lifespan, rather than simply burning out.
| Lamp Type | LED | Fluorescent | Halogen | Incandescent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Uses 80% less energy than incandescent | Uses 75% less energy than incandescent | Uses 30% less energy than incandescent | 90% of energy is wasted as heat |
| Annual Operating Costs | Low | Medium-Low | Medium | High |
| Average Life Span | 50,000 Hours | 10,000 Hours | 1,000 Hours | 1,000 Hours |
| Light Output (watts) | 6-8W | 13-15W | 45W | 60W |
| Color Temperature | Varies by product | 3,000K to 6,000K | 2,700K to 5,500K | 2,700K |
| Color Rendering Index | 80-90+ | 60-70+ | 100 | 100 |
| Dimmable | Most | Very Few | Yes | Yes |
Benefits & Disadvantages
Benefits:
Efficiency: Not just for show, the efficiency of LED technology is unmatched by all other lighting designs. LEDs only use about 20 percent as much electricity to produce the same amount of light and are more than five times as great as incandescent rivals. High-quality LED lights last anywhere from 20,000 to 50,000 hours with proper use and care. Essentially if you used the light for 6hours a day, 365 days a year, that light could last upwards of 20 years.
Brightness: For LEDs, the brightness is measured in lumens, whereas the energy the bulb itself consumes is still measured in watts. In order to produce the same amount of light, LED and fluorescent bulbs consume much fewer watts than incandescent or halogen bulbs. A standard 60W incandescent produces 800 lumens, whereas an LED light would consume only around 15 watts to produce the same 800 lumens.
Lifespan: LED technology is so efficient and powerful that bulbs do not burn out like a standard lamp, so individual diodes do not need to be replaced. Instead, they generally produce lower output levels over a long period of time. An LED is usually considered “dead” at 70% of its initial light output.
LED vs. Fluorescents: Both LED and fluorescent lighting offer more efficiency than incandescent. LEDs consume up to 90% less energy while fluorescents consume up to 75% less.
Disadvantages:
Cost: LEDs do have an initial higher cost compared to traditional lamps, but the cost is quickly made up within a few years thanks to the energy efficiency and long lifespan. Earlier technology also emitted only directional light making most LEDs better suited for task lighting as they did not offer a proper ambient glow. Today LED luminaries are omni-directional and point light through high-quality lenses to give off a balanced and properly diffused glow.
The components of LEDs are quite costly: circuit boards, drivers, and some utilize yellow phosphor, which is a rare earth compound. However, with the increasing advances in technology and an increase in popularity, the prices continue to drop. As LEDs offer different qualities of light, the costs can differ as well, look for ones that provide the best color and light output over time from top manufacturers.
Color Temperature:
What does warm and cool lighting mean for LEDs?
When discussing warm and cool lighting, it is in reference to the LED color temperature in relation to the Kelvin Color Temperature Scale. LEDs with a Temperature of 2700K produce a very warm, almost golden white light while closer to the top of the scale, 7000K is a very cool white light that can even appear to have a light blue tint. 3000K is a pleasantly soft warm white, 3500K or 4000K is in the range of bright warm white, and beyond that it becomes bright cool white.
So which is best for your space? Personal tastes will always vary, but less than 2700K is typically used in areas where a bright light is not needed – perhaps an accent lamp in the living room whose sole purpose is to provide a warming glow. 2700K to 3500K will produce a moderately warming glow and can be used to light most rooms of the home where ambiance is important such as the dining room or living room. Lighting starts to appear as a natural white around 4000K, which is ideal for task lighting or direct overhead lighting, so spaces like kitchens tend to be between 3500K-5000K depending on the homeowner’s preference for warm versus cool lighting. LED lighting over 5000K is rarely going to be used in the home, but is very common in commercial settings.
Best Uses
Today, LEDs can be used in a wide variety of lighting designs all throughout your home. From kitchen pendants to landscape bollards, LED lighting can provide welcoming illumination in a myriad of spaces. A great advantage of LEDs is their excellent directionality, so they are a perfect option for:
- Under cabinet lighting
- Chandeliers
- Recessed lighting
- Task and reading Lamps
- Hard to reach places ( thanks to their long lifespan)
- Picture/Art Lighting (does not produce UV radiation and is safe for artwork)
- Stair and path lighting
- Hallway lighting
With more and more lighting fixtures being outfitted with integrated LEDs – meaning the lighting is built right into the fixture, so no changing of bulbs is needed, all lamping stats should be provided upfront since there is no option for alternative bulbs. For any fixture where you are providing the bulb yourself, look for the necessary information on the packaging of the bulb.